| References |
| Synonyms |
|
| Stability |
1 year |
| Storage |
-80°C |
| Shipping |
Dry ice
in continental US; may vary elsewhere
|
Background Reading
Muccioli, G.G., Labar, G., and Lambert, D.M. CAY10499, a novel monoglyceride lipase inhibitor evidenced by an expeditious MGL assay. ChemBioChem 9 2704-2710 (2008).
Stella, N., Schweitzer, P., and Piomelli, D. A second endogenous cannabinoid that modulates long-term potentiation. Nature 388 773-778 (1997).
Sugiura, T., Kodaka, T., Kondo, S., et al. 2-Arachidonoylglycerol, a putative endogenous cannabinoid receptor ligand, induces rapid, transient elevation of intracellular free Ca2+ in neuroblastoma X glioma hybrid NG108-15 cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 229 58-64 (1996).
Kondo, S., Kondo, H., Nakane, S., et al. 2-Arachidonoylglycerol, an endogenous cannabinoid receptor agonist: Identification as one of the major species of monoacylglycerols in various rat tissues, and evidence for its generation through Ca2+-dependent and -independent mechanisms. FEBS Lett 429 152-156 (1998).
Rodríguez De Fonseca, F., Del Arco, I., Bermudez-Silva, F., et al. The endocannabinoid system: Physiology and pharmacology. Alcohol Alcohol 40(1) 2-14 (2005).
Dinh, T.P., Carpenter, D., Leslie, F.M., et al. Brain monoglyceride lipase participating in endocannabinoid inactivation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99(16) 10819-10824 (2002).
Lambert, D.M., and Fowler, C.J. The endocannabinoid system: Drug targets, lead compounds, and potential therapeutic applications. J Med Chem 48(16) 5059-5087 (2005).
Show all 7
Hide all but first 3
| Size |
Global Purchasing |
| 96 wells |
|
Description
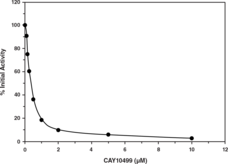
The endocannabinoid system is a ubiquitous lipid signaling system that is involved in various regulatory functions throughout the body. The main endocannabinoids are arachidonoyl ethanolamide (AEA) and 2-arachidonoyl glycerol (2-AG). They bind to G protein-coupled receptors, of which the cannabinoid (CB1) receptor is densely distributed in areas of the brain related to motor control, cognition, emotional responses, and homeostasis.1,2,3,4 Acting via the CB2 receptor in the peripheral tissues, the endocannabinoid system is one of the crucial modulators of the autonomic nervous system, the immune system, and microcirculation. Endocannabinoids are released upon demand from lipid precursors in a receptor-dependent manner. They are transported into cells by an apparently specific uptake system and degraded primarily by two enzymes, fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH) and monoacylglycerol lipase (MAGL) resulting in the termination of their biological actions.5 FAAH, a serine hydrolase, can degrade many fatty acid amides, including AEA. Although FAAH can hydrolyze 2-AG, the main enzyme responsible for the inactivation of this monoglyceride is another serine hydrolase, MAGL. Finding inhibitors to these endocannabinoid hydrolases could offer another approach in the treatment of pain, obesity, and various neurological diseases, where higher endocannabinoid activity would be beneficial. An advantage of such enzyme inhibition over direct cannabinoid agonists could result in higher selectivity, as it would increase activity of the endocannabinoid system only at sites where on-going production of endocannabinoids is taking place.6 Cayman’s Monoacylglycerol Lipase Inhibitor Screening Assay provides a convenient method for screening human MAGL inhibitors. MAGL hydrolyzes 4-nitrophenylacetate resulting in a yellow product, 4-nitrophenol, with an absorbance of 405-412 nm.7
1
Stella, N., Schweitzer, P., and Piomelli, D. A second endogenous cannabinoid that modulates long-term potentiation. Nature 388 773-778 (1997).
2
Sugiura, T., Kodaka, T., Kondo, S., et al. 2-Arachidonoylglycerol, a putative endogenous cannabinoid receptor ligand, induces rapid, transient elevation of intracellular free Ca2+ in neuroblastoma X glioma hybrid NG108-15 cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 229 58-64 (1996).
3
Kondo, S., Kondo, H., Nakane, S., et al. 2-Arachidonoylglycerol, an endogenous cannabinoid receptor agonist: Identification as one of the major species of monoacylglycerols in various rat tissues, and evidence for its generation through Ca2+-dependent and -independent mechanisms. FEBS Lett 429 152-156 (1998).
4
Rodríguez De Fonseca, F., Del Arco, I., Bermudez-Silva, F., et al. The endocannabinoid system: Physiology and pharmacology. Alcohol Alcohol 40(1) 2-14 (2005).
5
Dinh, T.P., Carpenter, D., Leslie, F.M., et al. Brain monoglyceride lipase participating in endocannabinoid inactivation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99(16) 10819-10824 (2002).
6
Lambert, D.M., and Fowler, C.J. The endocannabinoid system: Drug targets, lead compounds, and potential therapeutic applications. J Med Chem 48(16) 5059-5087 (2005).
7
Muccioli, G.G., Labar, G., and Lambert, D.M. CAY10499, a novel monoglyceride lipase inhibitor evidenced by an expeditious MGL assay. ChemBioChem 9 2704-2710 (2008).
|