| References |
| Synonyms |
|
| Formal Name |
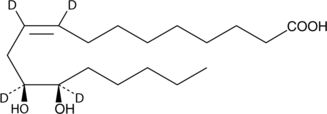
(±)12,13-dihydroxy-9Z-octadecenoic-9,10,12,13-d4 acid |
| Molecular Formula |
C18H30D4O4 |
| Formula Weight |
318.5 |
| Formulation |
A solution in methyl acetate |
| Purity |
≥99% deuterated product |
| Stability |
1 year |
| Storage |
-20°C |
| Shipping |
Wet ice
in continental US; may vary elsewhere
|
| SMILES |
CCCCC[C@@H]([2H])(O)[C@@H]([2H])(O)CC(=C([2H])/CCCCCCCC(=O)O)[2H]
|
Background Reading
Moran, J.H., Weise, R., Schnellmann, R.G., et al. Cytotoxicity of linoleic acid diols to renal proximal tubular cells. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 146 53-59 (1997).
Jude, A.R., Little, J.M., Czernik, P.J., et al. Glucuronidation of linoleic acid diols by human microsomal and recombinant UDP-glucuronosyltransferases: Identification of UGT2B7 as the major isoform involved. Arch Biochem Biophys 389(2) 176-186 (2001).
Markaverich, B.M., Crowley, J.R., Alejandro, M.A., et al. Leukotoxin diols from ground corncob bedding disrupt estrous cyclicity in rats and stimulate MCF-7 breast cancer cell proliferation. Environ Health Perspect 113(12) 1698-1704 (2005).
Moran, J.H., Nowak, G., and Grant, D.F. Analysis of the toxic effects of linoleic acid, 12,13-cis-epoxyoctadecenoic acid, and 12,13-dihydroxyoctadecenoic acid in rabbit renal cortical mitochondria. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 172 150-161 (2001).
Show all 4
Hide all but first 3
| Size |
Global Purchasing |
| 25 µg |
|
| 50 µg |
|
| 100 µg |
|
| 250 µg |
|
Description
(±)12,13-DiHOME is the diol resulting from the soluble epoxide hydrolase opening of (±)12,13-EpOME. The mixture of the methyl ester of this diol and the 9,10 isomer are more cytotoxic than the methyl ester epoxides in renal proximal tubular cells.1 However, in renal cortical mitochondria, the conversion of the epoxide to 12,13-DiHOME appears to be part of the detoxification pathway that prevents mitochondrial dysfunction.2 This diol and the 9,10 isomer can be glucuronidated by human liver and intestinal microsomes as well as recombinant UGT2B7 through a hydroxyl group. High levels of LA-diol glucuronides have been found in the urine of humans with peroxisomal diseases.3 A mixture of the diols stimulates breast cancer cell proliferation in vitro and disrupts reproductive function in rats at relatively low concentrations.4
1
Moran, J.H., Weise, R., Schnellmann, R.G., et al. Cytotoxicity of linoleic acid diols to renal proximal tubular cells. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 146 53-59 (1997).
2
Moran, J.H., Nowak, G., and Grant, D.F. Analysis of the toxic effects of linoleic acid, 12,13-cis-epoxyoctadecenoic acid, and 12,13-dihydroxyoctadecenoic acid in rabbit renal cortical mitochondria. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 172 150-161 (2001).
3
Jude, A.R., Little, J.M., Czernik, P.J., et al. Glucuronidation of linoleic acid diols by human microsomal and recombinant UDP-glucuronosyltransferases: Identification of UGT2B7 as the major isoform involved. Arch Biochem Biophys 389(2) 176-186 (2001).
4
Markaverich, B.M., Crowley, J.R., Alejandro, M.A., et al. Leukotoxin diols from ground corncob bedding disrupt estrous cyclicity in rats and stimulate MCF-7 breast cancer cell proliferation. Environ Health Perspect 113(12) 1698-1704 (2005).
|