服务热线
021-60498804
产品中心
/ Products Classification 点击展开+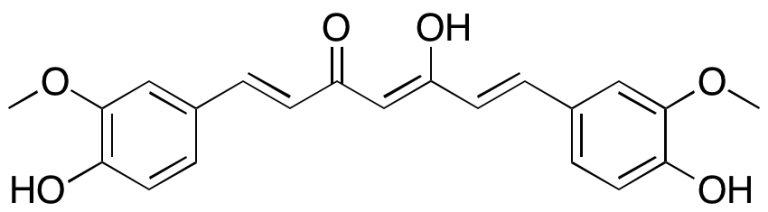
| Cat. Number | C8069 |
| Chemical Name | C8069 CURCUMIN 458-37-7 |
| CAS Number | 458-37-7 |
| Mol. Formula | C21H20O6 |
| Mol. Weight | 368.38 |
| Qty 1 |
5g |
| Qty 2 | 50g |
| Appearance | Orange-yellow powder |
| Application Notes | ≥97% curcuminoid content |
| Synonym | Turmeric yellow |
| Melting Pt. | 183°C |
| Solubility | Insoluble in water. Soluble in ethanol (10 mg/mL), DMSO (74 mg/mL), chloroform, acetone, DMF. Soluble in 0.1 M NaOH to 3 mg/mL-do not store more than 12 hours. |
| Storage condition | Ambient |
| References | Curcumin is the active component of turmeric, a member of the ginger family. Curcumin is a diarylheptanoid; it displays a wide variety of health benefits, including antioxidative, anticancer chemotherapeutic, antifungal, antibiotic, and atherosclerotic prophylactic activities. In an animal model of running-induced oxidative damage, curcumin decreases NADPH-oxidase mRNA and hydrogen peroxide levels, decreasing oxidative stress. Curcumin increases levels of APOBEC1, increasing beneficial ApoB-48 and decreasing harmful ApoB-100, facilitating increased clearance of lipid particles from plasma in vitro. In cellular models of cancer, curcumin activates mammalian sterile 20-like kinase 1 (MST1), activating JNK and inducing apoptosis. In cellular models of glioma, curcumin downregulates expression of sonic hedgehog (Shh), Smo, GLI1, cyclin D1, and Bcl-2, inhibiting proliferation and migration and increasing apoptosis; in related animal models, curcumin decreases tumor volume and prolongs survival. In an animal model of Alzheimer’s disease utilizing the Morris water maze, curcumin rescues cognitive deficits by inhibiting collapsing response mediator protein 2 (CRMP2) and protecting against amyloid-β (Aβ)-induced hippocampal damage. This compound inhibits fMLP- and LPS-induced suppression of neutrophil apoptosis by preventing activation of NF-κB and decreasing production of pro-inflammatory mediators such as IL-6, IL-8, MIP-1α, and MIP-1β. Curcumin also displays antibacterial and antifungal activities, inhibiting cell wall biosynthesis of Candida albicans in vitro. ReferencesKawanishi N, Kato K, Takahashi M, et al. Curcumin attenuates oxidative stress following downhill running-induced muscle damage. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2013 Nov 22;441(3):573-8. PMID: 24184481. Du WZ, Feng Y, Wang XF, et al. Curcumin Suppresses Malignant Glioma Cells Growth and Induces Apoptosis by Inhibition of SHH/GLI1 Signaling Pathway in Vitro and Vivo. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2013 Dec;19(12):926-36. PMID: 24165291. Tian N, Li X, Luo Y, et al. Curcumin regulates the metabolism of low density lipoproteins by improving the C-to-U RNA editing efficiency of apolipoprotein B in primary rat hepatocytes. Mol Med Rep. 2013 Oct 24. [Epub ahead of print]. PMID: 24173373. Wang Y, Yin H, Li J, et al. Amelioration of β-amyloid-induced cognitive dysfunction and hippocampal axon degeneration by curcumin is associated with suppression of CRMP-2 hyperphosphorylation. Neurosci Lett. 2013 Oct 21. [Epub ahead of print]. PMID: 24157857. Antoine F, Simard JC, Girard D. Curcumin inhibits agent-induced human neutrophil functions in vitro and lipopolysaccharide-induced neutrophilic infiltration in vivo. Int Immunopharmacol. 2013 Oct 21. [Epub ahead of print]. PMID: 24157330. Gunes H, Gulen D, Mutlu R, et al. Antibacterial effects of curcumin: an in vitro minimum inhibitory concentration study. Toxicol Ind Health. 2013 Oct 21. [Epub ahead of print]. PMID: 24097361. Kumar A, Dhamgaye S, Maurya IK, et al. Curcumin targets cell wall integrity via calcineurin mediated signaling in Candida albicans. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2013 Oct 21. [Epub ahead of print]. PMID: 24145527. Yu T, Ji J, Guo YL. MST1 activation by curcumin mediates JNK activation, Foxo3a nuclear translocation and apoptosis in melanoma cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2013 Oct 14. [Epub ahead of print]. PMID: 24134840. Narayanan N, Nargi D, Randolph C, et al. Liposome encapsulation of curcumin and resveratrol in combination reduces prostate cancer incidence in PTEN knockout mice. Int J Cancer. 2009Feb 6;125(1):1-8. PMID: 19326431. Perry MC, Demeule M, Regina A, et al. Curcumin inhibits tumor growth and angiogenesis in glioblastoma xenografts. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2010 Aug;54(8):1192-1201. PMID: 20087857. Martin RC, Aiyer HS, Malik D, Li Y. Effect on pro-inflammatory and antioxidant genes and bioavailable distribution of whole turmeric vs curcumin: similar root but different effects. Food Chem Toxicol. 2012 Feb;50(2):227-231. PMID: 22079310. |
下一个:ENTINOSTAT上一个:CAMBINOL |
|





