| References |
| Synonyms |
- Peroxisome Proliferator-activated Receptor γ Full Length (human recombinant)
|
| Formulation |
A solution in 20 mM Tris HCl, pH 8.0, containing 250 mM KCl, 20% glycerol, 5 mM DTT, and 0.5 mM EDTA |
| Purity |
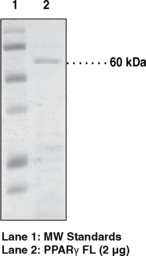
>90% by SDS-PAGE |
| Stability |
6 months |
| Storage |
-80°C |
| Shipping |
Dry ice
in continental US; may vary elsewhere
|
Background Reading
Kersten, S., Desvergne, B., and Wahli, W. Roles of PPARs in health and disease. Nature 405 421-424 (2000).
Vidal-Puig, A., Jimenez-Linan, M., Lowell, B.B., et al. Regulation of PPAR γ gene expression by nutrition and obesity in rodents. J Clin Invest 97 2553-2561 (1996).
Clark, R.B. The role of PPARs in inflammation and immunity. J Leukoc Biol 71 388-400 (2002).
| Size |
Global Purchasing |
| 5 µg |
|
| 10 µg |
|
| 25 µg |
|
| 50 µg |
|
Description
Source:
human recombinant N-terminal His-tagged protein expressed in E. coli
·
Mr:
~60 kDa
·
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors (PPARs) are members of the nuclear receptor family of ligand activated transcription factors that heterodimerizes with retinoic acid-like receptors to regulate gene expression and differentiation.1 The PPAR family of nuclear hormone receptors consists of three subtypes encoded by separate genes: PPARα, PPARδ (also referred to as hNUC1, PPARβ, or FAAR), and PPARγ. Among them PPARγ is the most widely studied and has been implicated in the pathology of numerous diseases including obesity, diabetes, atherosclerosis, and cancer.2 PPARγ is primarily expressed in adipose tissue and to a lesser extent in the colon, immune system, and the retina.3 The functionality of the DNA binding domain (DBD) was tested using Cayman’s PPARγ Transcription Factor Assay (Catalog no. 10006855). The purity was determined using gel electrophoresis followed by coomassie staining. The ligand binding domain functionality was confirmed using a fluorescent displacement assay with ANS and Rosiglitazone.
1
Kersten, S., Desvergne, B., and Wahli, W. Roles of PPARs in health and disease. Nature 405 421-424 (2000).
2
Vidal-Puig, A., Jimenez-Linan, M., Lowell, B.B., et al. Regulation of PPAR γ gene expression by nutrition and obesity in rodents. J Clin Invest 97 2553-2561 (1996).
3
Clark, R.B. The role of PPARs in inflammation and immunity. J Leukoc Biol 71 388-400 (2002).
|