| References |
| Synonyms |
- Lecithin:Cholesterol Acyltransferase
- Phosphatidylcholine-Sterol O-Acyltransferase
|
| Formulation |
Peptide affinity-purified IgG |
| Stability |
1 year |
| Storage |
-20°C |
| Shipping |
Wet ice
in continental US; may vary elsewhere
|
| Specificity |
| Human LCAT |
+ |
| Murine LCAT |
+ |
| Porcine LCAT |
+ |
| Bovine LCAT |
+ |
Show all 4
Hide all but first 3
|
Background Reading
Linsel-Nitschke, P., and Tall, A.R. HDL as a target in the treatment of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. Nat Rev Drug Discov 4 193-205 (2005).
McLean, J., Fielding, C., Drayna, D., et al. Cloning and expression of human lecithin-cholesterol acyltransferase cDNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 83 2335-2339 (1986).
Chisholm, J.W., Gebre, A.K., and Parks, J.S. Characterzation of C-terminal histidine-tagged human recombinant lecithin: Cholesterol acyltransferase. J Lipid Res 40 1512-1519 (1999).
Marcel, Y.L., Vézina, C.A., Weech, P.K., et al. Lecithin: Cholesterol Acyltransferase, a review and immunochemical studies. Adv Exp Med Biol 201 163-179 (1986).
Glomset, J.A. Physiological role of lecithin cholesterol acyltransferase. Am J Clin Nutr 23(8) 1129-1136 (1970).
Show all 5
Hide all but first 3
| Size |
Global Purchasing |
| 500 µl |
|
Description
Antigen:
human LCAT protein amino acids 132-143 (SVEYLDSSKLAG)
·
Host:
rabbit
·
Application(s):
WB; other applications not tested
·
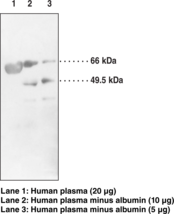
Lecithin:cholesterol acyltransferase (LCAT) has both phospholipase and acyltransferase activities. LCAT catalyzes the fatty acid transfer from the sn-2 position of phosphatidylcholine (lecithin) to cholesterol and to a lesser degree to other acceptor molecules.1,2 This enzyme is critical to the process of reverse cholesterol transport or movement of cholesterol esters into high density lipoprotein (HDL) particles from cells.3 LCAT is abundant in blood-plasma, however it is present in other fluids and tissues such as ovary. This protein may be detected on immunoblot at 49.5 kDa as well as at 66 kDa when fully glycosylated.4,5 Plasma samples should be diluted prior to electrophoresis and immunoblotting to avoid the band-broadening effect caused by comigration with endogenous albumin.
1
Glomset, J.A. Physiological role of lecithin cholesterol acyltransferase. Am J Clin Nutr 23(8) 1129-1136 (1970).
2
McLean, J., Fielding, C., Drayna, D., et al. Cloning and expression of human lecithin-cholesterol acyltransferase cDNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 83 2335-2339 (1986).
3
Linsel-Nitschke, P., and Tall, A.R. HDL as a target in the treatment of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. Nat Rev Drug Discov 4 193-205 (2005).
4
Marcel, Y.L., Vézina, C.A., Weech, P.K., et al. Lecithin: Cholesterol Acyltransferase, a review and immunochemical studies. Adv Exp Med Biol 201 163-179 (1986).
5
Chisholm, J.W., Gebre, A.K., and Parks, J.S. Characterzation of C-terminal histidine-tagged human recombinant lecithin: Cholesterol acyltransferase. J Lipid Res 40 1512-1519 (1999).
|