服务热线
021-60498804
产品中心
/ Products Classification 点击展开+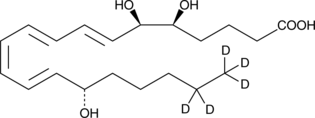
| Cat. Number | 652579101856487 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Name | 5(S),6(R)-Lipoxin A4-d5 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| References |
Background ReadingMaddox, J.F., and Serhan, C.N. Lipoxin A4 and B4 are potent stimuli for human monocyte migration and adhesion: Selective inactivation by dehydrogenation and reduction. J Exp Med 183 137-146 (1996). Ramstedt, U., Serhan, C.N., Nicolaou, K.C., et al. Lipoxin A- Serhan, C.N., Nicolaou, K.C., Webber, S.E., et al. Lipoxin A. Stereochemistry and biosynthesis. J Biol Chem 261 16340-16345 (1986). Serhan, C.N., Hamberg, M., and Samuelsson, B. Lipoxins: Novel series of biologically active compounds formed from arachidonic acid in human leukocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 81 5335-5339 (1984). Show all 4 Hide all but first 3
Description
5(S),6(R)-
1 Serhan, C.N., Nicolaou, K.C., Webber, S.E., et al. Lipoxin A. Stereochemistry and biosynthesis. J Biol Chem 261 16340-16345 (1986). 2 Serhan, C.N., Hamberg, M., and Samuelsson, B. Lipoxins: Novel series of biologically active compounds formed from arachidonic acid in human leukocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 81 5335-5339 (1984).
3
Ramstedt, U., Serhan, C.N., Nicolaou, K.C., et al. Lipoxin A- 4 Maddox, J.F., and Serhan, C.N. Lipoxin A4 and B4 are potent stimuli for human monocyte migration and adhesion: Selective inactivation by dehydrogenation and reduction. J Exp Med 183 137-146 (1996). |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||





